COM Port
The cluster communication port is the COM port, referred to as the serial port. The serial port on the microcomputer is usually 9-pin, but also has a 25-pin interface, and the maximum rate is 115200bps.
It is usually used to connect serial mice and communication equipment (such as connecting external modems for data communication or CNC machine interface in some factories), etc.

COM Port
The COM interface refers to the cluster communication port interface, that is, the serial communication port.
The serial port is called the serial interface, and the current PC generally has two serial ports COM 1 and COM 2.
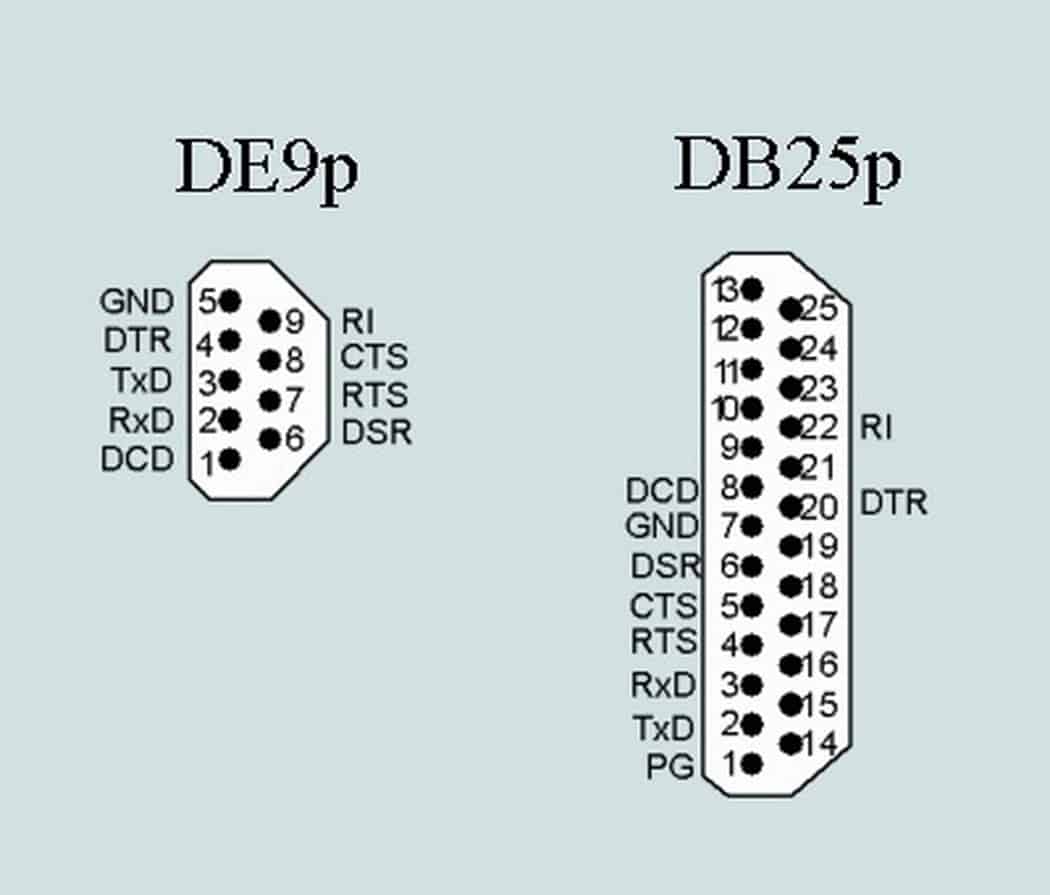
Usually, COM 1 uses a 9-pin D-shaped connector, also known as the RS-232 interface, while COM 2 uses an old-fashioned DB25-pin connector, also known as the RS-422 interface, which has been rarely used.
They follow the MODBUS communication protocol. Generally, households do not use this interface, and the computer serial port (COM1) is used for RS232 or 485 communication with the instrument to collect data on the embedded industrial pc control.
A serial port differs from a parallel port in that its data and control information is transmitted bit by bit. Although the speed will be slower, the transmission distance is longer than the parallel port, so if you want to communicate over a long distance, you should use the serial port.
Generally, there are two chassis, but the new chassis may only have one. Laptops probably don’t.
There are many industrial instruments that use it as a standard communication port. The content and format of the communication are generally attached to the user manual of the instrument.
Level regulation
There are two ways of serial communication and parallel communication for data transmission between computers or between computers and terminals. Because the serial communication method has fewer lines and low cost, especially in long-distance transmission, it avoids the inconsistency of the characteristics of multiple lines and is widely used.
In serial communication, both communication parties are required to adopt a standard interface, so that different devices can be easily connected for communication.
RS-232-C interface (also known as EIA RS-232-C) is the most commonly used serial communication interface at present. It is a standard for serial communication jointly formulated by the Electronic Industries Association (EIA) in conjunction with Bell System, modem manufacturers, and computer terminal manufacturers in 1970.
Its full name is “Technical Standard for Serial Binary Data Exchange Interface between Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and Data Communication Equipment (DCE)”. This standard stipulates that a 25-pin DB25 connector is used, and each pin The signal content of the pin is specified, and the level of various signals is also specified.
Serial interface
A motherboard generally has two COM serial ports, and the serial ports are divided according to electrical standards and protocols, including RS-232-C, RS-422, RS485, USB, etc. The RS-232-C, RS-422, and RS-485 standards only stipulate the electrical characteristics of the interface and do not involve connectors, cables, or protocols.
USB is a new interface standard developed in recent years, mainly used in the field of high-speed data transmission.
RS-232-C
Also known as a standard serial port, it is the most commonly used serial communication interface at present. It is a standard for serial communication formulated by the American Electronics Industries Association (EIA) in conjunction with Bell System, modem manufacturers, and computer terminal manufacturers in 1970.
Its full name is “Technical Standard for Serial Binary Data Exchange Interface between Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and Data Communication Equipment (DCE)”. The traditional RS-232-C interface standard has 22 wires and uses a standard 25-core D-type plug socket. The simplified 9-core D-type socket has been used since IBM PC/AT. So far, the 25-pin socket has been rarely used in modern applications.
Computers generally have two serial ports: COM1 and COM2, and the 9-pin D-shaped interface is usually seen on the back of the computer. Now there are many mobile phone data lines or logistics receivers that use COM ports to connect to computers.

RS-422
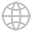
In order to improve the shortcomings of the short communication distance and low rate of RS-232, RS-422 defines a balanced communication interface, which increases the transmission rate to 10Mb/s and extends the transmission distance to 4000 feet (when the rate is lower than 100kb/s), And allows up to 10 receivers to be connected on a balanced bus.
RS-422 is a one-way, balanced transmission specification for single-machine transmission and multi-machine reception, named TIA/EIA-422-A standard.
RS-485
In order to expand the scope of application, EIA formulated the RS-485 standard on the basis of RS-422 in 1983, adding multi-point and two-way communication capabilities, that is, allowing multiple transmitters to be connected to the same bus, and adding transmitters at the same time The driving ability and conflict protection characteristics of the bus extend the common mode range of the bus, and it is named after the TIA/EIA-485-A standard.
Universal Serial Bus
USB, referred to as USB, is a widely used interface specification on computers at present. It is a new peripheral interface standard initiated by several major manufacturers such as Intel, Microsoft, Compaq, IBM, NEC, and Northern Telcom.
The USB interface is a four-pin interface on the computer motherboard, in which the two pins in the middle transmit data, and the two pins on both sides supply power to peripherals.
The USB interface is fast, easy to connect, does not require an external power supply, the transmission speed is 12Mbps, and the new USB 2.0 can reach 480Mbps; the maximum length of the cable is 5 meters, and the USB cable has 4 lines: 2 signal lines, 2 power lines, which can be provided 5-volt power supply, USB cables are divided into two types: shielded and unshielded, the transmission speed of shielded cables can reach 12Mbps, the price is more expensive, the speed of unshielded cables is 1.5Mbps, but the price is cheap; USB can connect up to 127 devices in series; Support hot swap. The latest specification is USB 4.0 with a maximum transfer speed of 40 Gbps.
Serial port use
The serial port on the computer motherboard: an interface for serial transmission, which can only transmit 1Bit at a time.
The serial port can be used to connect an external modem, plotter, or serial printer. It can also connect to network devices, such as routers and switches, as a console connection, mainly to configure them. Consumer electronics have replaced the serial interface with USB; but in non-consumer applications, such as network equipment, the serial interface is still the main transmission control method.
#没有设置高宽参数,将以原图输出) What is RS232
What is RS232
#没有设置高宽参数,将以原图输出) COM Port
COM Port
#没有设置高宽参数,将以原图输出) RS232 9 Pin Pinout: Here’s What You Need to Know
RS232 9 Pin Pinout: Here’s What You Need to Know
#没有设置高宽参数,将以原图输出) RS232 to RS422/485 Conversion
RS232 to RS422/485 Conversion





)